Imagine a world where treatments are as unique as the individuals receiving them. This is the promise of precision medicine, a revolutionary approach transforming prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Unlike traditional methods that apply a one-size-fits-all strategy, precision medicine focuses on the unique aspects of each individual—their genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
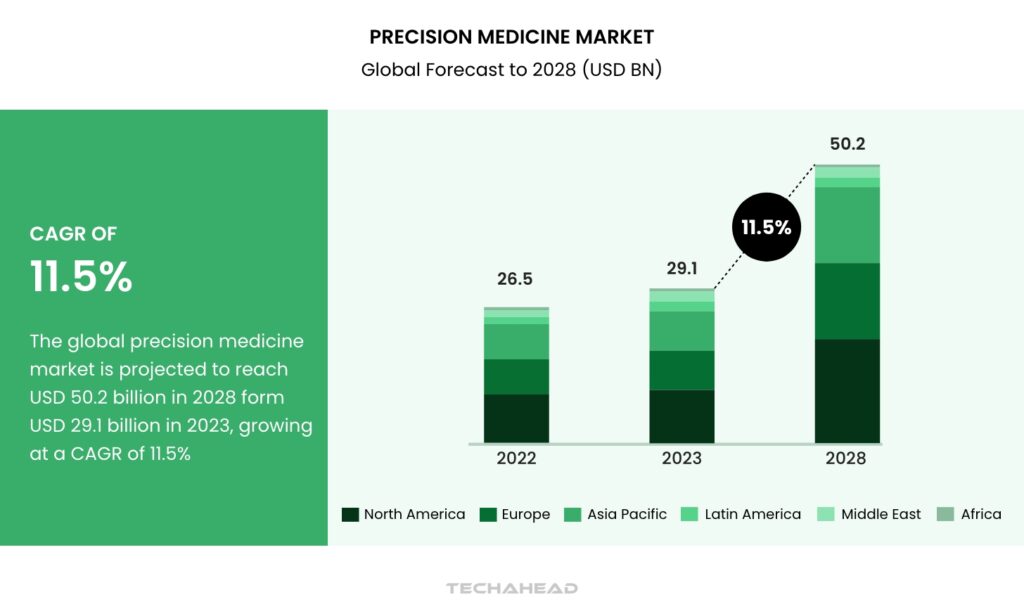
Precision medicine isn’t just reshaping how we treat diseases—it’s transforming the global healthcare industry. The market for precision medicine is projected to skyrocket from $29.1 billion in 2023 to $50.2 billion by 2028, fueled by an impressive CAGR of 11.5%. This exponential growth reflects the increasing adoption of targeted therapies, driven by breakthroughs in genomic research.
Consider the case of Emma, diagnosed with a complex condition requiring specialized care. Precision medicine, guided by her genetic data, crafted a treatment plan tailored specifically to her needs. The key to her successful outcome wasn’t just advanced technology but also the quality of the data used. Accurate and comprehensive genomic insights made all the difference.
The rise of genetic testing and companion diagnostics plays a pivotal role in this revolution. These tools allow for early and precise identification of conditions, enabling healthcare providers to implement highly effective interventions. Moreover, increasing approvals for personalized medicines from leading regulatory bodies are accelerating the adoption of precision medicine globally.
This surge is a testament to the growing recognition of the potential held by genetically targeted therapies. As the precision medicine industry continues to expand, it promises a future where every patient receives care tailored perfectly to their unique profile, revolutionizing the way we approach health and wellness
Precision Medicine Market
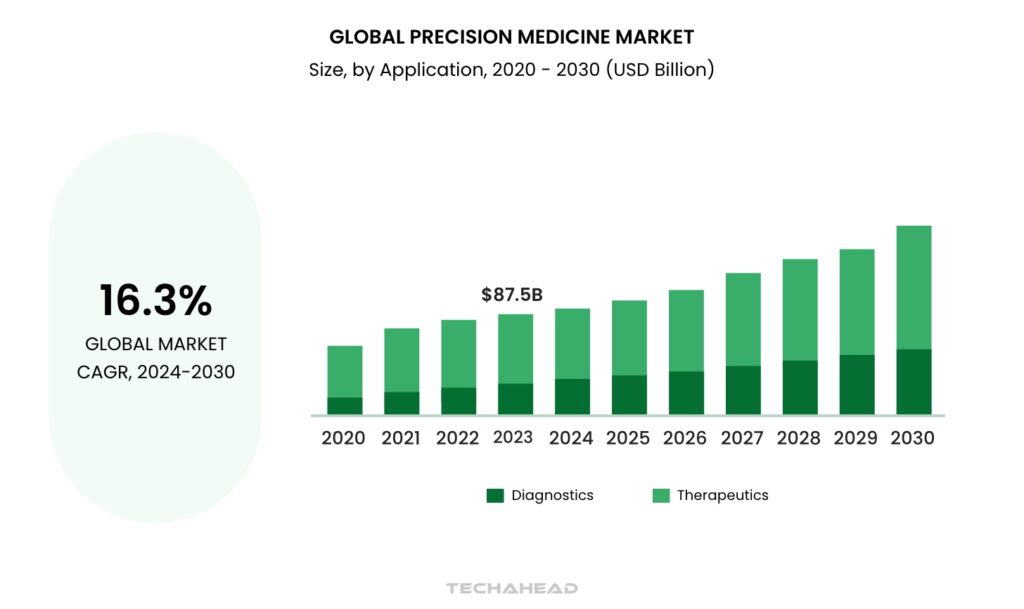
In 2023, the precision medicine market was valued at a staggering $87.50 billion. But this is just the beginning. Experts predict it will grow at an impressive CAGR of 16.3% from 2024 to 2030, signaling a seismic shift in how diseases are treated and prevented.
Global precision medicine market highlights
- The therapeutics segment accounted for $71.90 billion in revenue in 2023, making it the largest contributor.
- Diagnostics is the fastest-growing and most lucrative application segment during the forecast period.
- North America was the highest revenue-generating region in the precision medicine market in 2023.
- Among countries, Mexico is expected to register the highest CAGR between 2024 and 2030.
Vital Role of High-Quality in Precision Medicine
In precision medicine, the value of high-quality data is unparalleled. It serves as the backbone for accuracy, efficiency, and innovation. Here’s an in-depth look:
Accurate Diagnoses
Precision medicine relies heavily on robust data to ensure precise diagnoses, especially for rare or intricate diseases. Comprehensive patient data—ranging from genetic profiles to lifestyle factors—is essential to capture nuanced patterns. Missteps caused by unreliable data can lead to delayed treatments, exacerbated conditions, and even patient harm. High-quality datasets reduce diagnostic errors, providing a clearer pathway to effective care.
Personalized Treatments
Tailored therapies in precision medicine demand accurate genomic and clinical datasets. These datasets enable practitioners to develop treatment plans that align with individual genetic markers and health histories. Any inaccuracies here can result in treatments that fail to address the core issue, potentially triggering adverse reactions. Precision in this context ensures patients receive optimized care with minimal side effects, improving treatment outcomes dramatically.
Driving Research Advancements
The evolution of precision medicine hinges on the availability of structured, high-quality data. Research into disease pathways, treatment efficacies, and population health trends thrives on such datasets. Reliable data accelerates the discovery of novel therapies, fosters deeper understanding of disease mechanisms, and supports cost-efficient healthcare innovations. In essence, it creates a feedback loop where insights from quality data fuel better healthcare solutions.
Cost Efficiency
The financial benefits of high-quality data in precision medicine cannot be overlooked. Clean, accurate data eliminates redundancies in diagnostic procedures and prevents unnecessary treatments. This translates to savings for healthcare providers and patients alike. Additionally, by enabling early detection and prevention strategies, precision medicine lowers the long-term costs associated with chronic or advanced-stage diseases.
When precision medicine is supported by accurate, detailed data, its potential to transform healthcare becomes boundless.
Navigating Data Quality Challenges in Precision Medicine
As precision medicine advances, ensuring data quality becomes a formidable challenge. These obstacles, rooted in data growth, complexity, and management, require strategic and comprehensive approaches. Here’s a detailed look:
Data Fragmentation
Data fragmentation arises when information is scattered across diverse systems and formats. This fragmentation creates barriers to seamless data access and integration. For example, clinical records might reside in legacy systems, while genomic data could be stored in cloud platforms. These disconnected datasets complicate analysis, delay insights, and reduce the efficiency of research and patient care. Bridging these gaps demands advanced interoperability solutions and standardized formats.
Data Silos
Data silos occur when information remains isolated in systems incompatible with others. These silos hinder collaboration, limit data-sharing, and slow down research progress. For instance, a hospital’s proprietary electronic health record may not integrate with national health databases. Overcoming silos requires robust data harmonization techniques and frameworks that promote interconnectivity while preserving individual system functionalities.
Data Incompleteness
Incomplete datasets lead to skewed analyses and flawed outcomes. Missing details—such as gaps in patient medical histories or unrecorded lifestyle factors—can distort results and impact patient care. These gaps not only affect diagnosis and treatment but also undermine the reliability of research studies. Enhancing data collection processes and deploying intelligent systems to identify and fill missing information are critical to addressing this issue.
Data Bias
Bias in datasets skew the representation of populations, leading to unfair or inaccurate outcomes. For example, underrepresentation of certain ethnic groups in genomic studies results in inequitable treatment recommendations. This bias perpetuates healthcare disparities and reduces the effectiveness of precision medicine. Tackling bias requires diverse, representative data sources and algorithms designed to account for systemic inequalities.
Data Privacy and Security
Patient data privacy and security are paramount in precision medicine. Unauthorized access or breaches can lead to compromised trust and regulatory penalties. For example, the need to share patient information for research often conflicts with stringent privacy laws. Implementing strong encryption methods, secure sharing protocols, and compliance frameworks can safeguard sensitive information while supporting innovation.
Addressing these interconnected challenges is essential to unlocking the full potential of precision medicine. High-quality data not only drives innovation but also ensures equitable and effective healthcare solutions.
Effective Strategies to Enhance Data Quality in Precision Medicine
Addressing data quality challenges in precision medicine demands a multifaceted approach. Implementing a combination of strategies ensures improved accuracy, consistency, and utility of data for personalized healthcare.
Here’s an expanded look at these strategies:
Standardization of Data Formats and Terminologies
Data diversity across sources often results in varied formats and terminologies. For example, one system might label a condition differently from another, complicating interoperability. Standardizing these elements ensures seamless data integration and analysis. This involves adopting universal healthcare coding standards like SNOMED CT or HL7 FHIR, which facilitate efficient data sharing and accurate research outcomes.
Data Cleaning and Validation
Errors and inconsistencies are common in raw data sets. Data cleaning involves identifying and rectifying these inaccuracies, while validation ensures the data aligns with predefined standards. For instance, correcting duplicate patient entries or filling in missing demographic details enhances reliability. Automated tools and machine learning algorithms can streamline this process, ensuring datasets are both accurate and complete.
Data Integration and Harmonization
Data collected from diverse sources often varies in collection methods and storage formats. Integration involves consolidating this data into a unified system, while harmonization ensures compatibility among datasets.
For example, aligning clinical trial data with electronic health records creates comprehensive datasets. These processes improve accuracy and enable holistic insights for precision medicine applications.
Data Governance and Ethics
Establishing robust governance frameworks ensures responsible data management. Governance policies define how data is collected, accessed, and shared. Ethical guidelines ensure patient information is handled transparently and securely. For instance, implementing consent-based data sharing upholds patient rights while fostering trust. Such practices are vital to maintaining the integrity of precision medicine initiatives.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transformative tools for enhancing data quality. Artificial intelligence algorithms can detect hidden patterns, identify anomalies, and predict missing values. Machine learning automates tasks like data cleaning, significantly reducing manual efforts. For example, predictive models can flag erroneous medical records, enabling proactive corrections. These technologies enhance data accuracy and accelerate research advancements.
Conclusion
The next step in automated data discovery for precision medicine lies at the crossroads of advanced technology and practical healthcare needs.
New technologies are revolutionizing how we manage complex biological data. Quantum computing offers immense processing power to handle vast datasets, while federated learning ensures secure data analysis without compromising privacy. Synthetic biology is also paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in treatments, expanding the potential of precision medicine.
Healthcare is shifting toward real-world data integration and patient-focused approaches. By incorporating data from wearable devices, long-term patient records, and population studies, automated systems are becoming indispensable. The increasing demand for standardized and interoperable healthcare systems is driving the adoption of these solutions, signaling a transformative change in precision medicine.

FAQs
Precision medicine, or personalized medicine, revolutionizes healthcare by customizing prevention and treatment. It considers genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors, ensuring tailored interventions that maximize efficacy for individuals.
AI enhances precision medicine by identifying patient phenotypes with unique treatment responses or healthcare needs. Using advanced computational models, AI processes vast data, drawing actionable insights and enabling intelligent decision-making that aids clinicians in providing precise care.
AI strengthens clinical decision support systems, boosting diagnostic accuracy and optimizing treatment strategies in areas like cardiology. By leveraging machine learning, AI identifies high-risk patients, customizes interventions, and refines treatment plans, improving overall patient outcomes.
AI techniques in bioinformatics include a range of applications, such as protein folding prediction, viral protease cleavage forecasting, and gene expression analysis. These methods leverage data to advance understanding of complex biological systems and support medical discoveries.