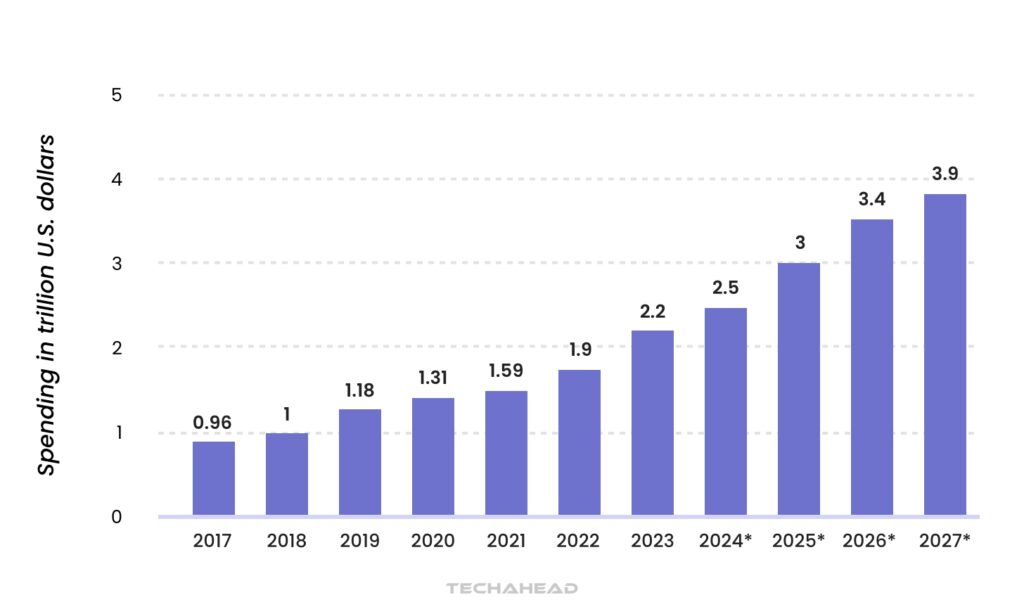
In 2024, global spending on digital transformation (DX) is projected to reach an astounding $2.5 trillion, with forecasts indicating it will soar to $3.9 trillion by 2027. This remarkable growth, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.1%, highlights the critical role technology plays in reshaping healthcare delivery.
Organizations are increasingly adopting digital gear along with telemedicine, EHRs, and wearable devices to improve patient person care & operational performance. The surge in DX spending displays a broader trend where businesses prioritize digitalization to stay competitive in an evolving digital landscape.
As we delve deeper into the implications of this transformation, it will become glaring that embracing digital health solutions isn’t simply useful but essential for modern-day healthcare structures aiming to enhance results and streamline services.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with telehealth services expanding significantly to meet the urgent demand for remote healthcare solutions. Digital health not only enhances patient access to care but also fosters personalized treatment through advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence.
By redefining innovation in healthcare, digital health is paving the way for more efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered services that promise to improve health outcomes globally. As we explore this dynamic field, it becomes clear that embracing digital health is essential for modernizing healthcare systems and addressing the evolving needs of patients.
The Rise of Digital Health Technologies in Modern Healthcare
The digital revolution is transforming healthcare, bringing unprecedented innovation & accessibility to medical services. As technology continues to advance, patients and healthcare providers are experiencing a paradigm shift in how medical care is delivered, monitored, and experienced.
Smartphone healthcare apps, wearable devices, and telemedicine platforms are breaking down traditional barriers, enabling real-time health tracking, remote consultations, and personalized medical insights. These digital health technologies empower individuals to take a more proactive approach to their wellness, offering tools that monitor everything from heart rate and sleep patterns to chronic disease management.
Hospitals and clinics are leveraging artificial intelligence and big data analytics to improve diagnostic accuracy, streamline administrative processes, and develop more targeted treatment plans. From AI-powered diagnostic tools to remote patient monitoring systems, the integration of digital technologies is creating a more responsive, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare ecosystem that promises to revolutionize medical practice and improve health outcomes globally.
Key Components of Digital Health: From Telemedicine to Wearables
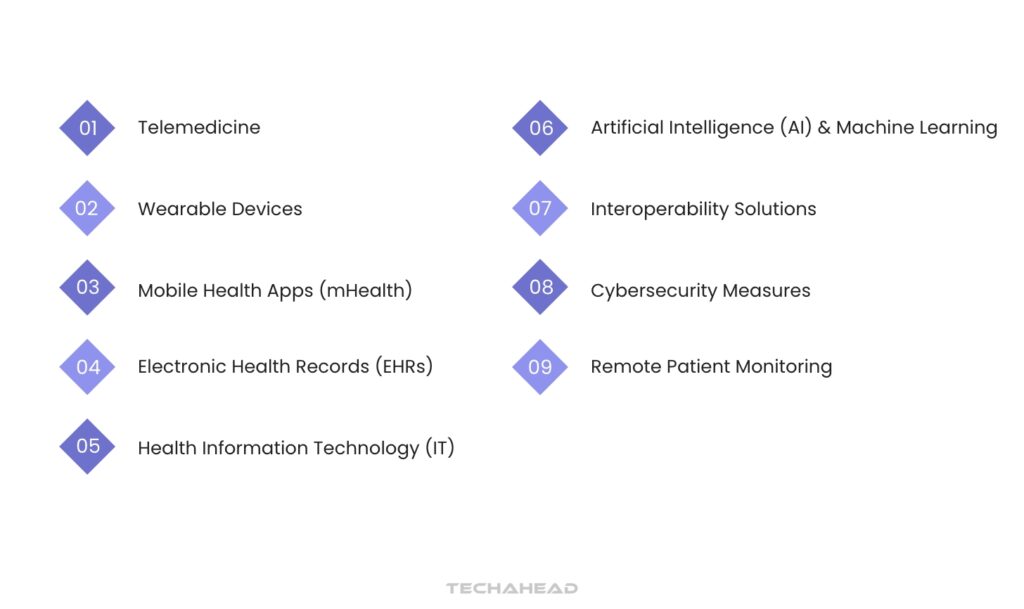
Telemedicine
Enables remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers, improving access to care and reducing the need for in-person visits.
Wearable Devices
Track vital signs and health metrics in real-time, empowering patients to monitor their health and share data with providers for better management of chronic conditions.
Mobile Health Apps (mHealth)
Provide users with tools for symptom tracking, medication reminders, and health education, fostering proactive health management.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Centralize patient information, allowing for seamless sharing among healthcare providers to enhance coordination of care.
Health Information Technology (IT)
Supports the storage, retrieval, and analysis of health data, facilitating informed decision-making and improving patient outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Analyze large datasets to identify patterns, predict health trends, and support clinical decision-making.
Interoperability Solutions
Ensure different digital health systems can communicate effectively, enhancing data sharing and collaboration across healthcare settings.
Cybersecurity Measures
Protect sensitive patient data from breaches and ensure compliance with regulations, safeguarding patient privacy.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Utilizes technology to continuously track patients’ health outside of traditional clinical settings, enabling timely interventions.
How Digital Health is Enhancing Patient Care & Experience
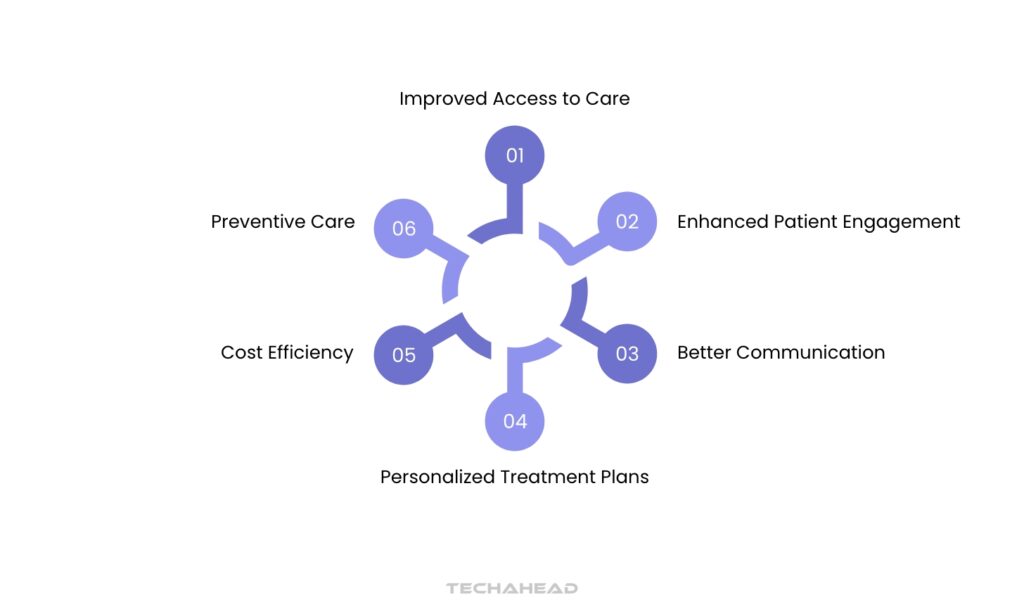
Improved Access to Care
Digital health tools, such as telemedicine, enable patients to consult healthcare providers remotely, significantly increasing access to care, especially for those in underserved areas.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
Mobile apps and patient portals empower individuals to actively manage their health by providing access to medical records, appointment scheduling, and personalized health reminders.
Better Communication
Digital platforms facilitate real-time communication between patients and providers, allowing for quicker responses to health inquiries and fostering stronger patient-doctor relationships.
Personalized Treatment Plans
With data analytics and wearable devices, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans based on individual health metrics, leading to more effective care.
Cost Efficiency
By reducing the need for in-person visits and enabling proactive health management, digital health can lower overall healthcare costs for both patients and providers.
Preventive Care
Digital health technologies allow for early detection of potential health issues through symptom tracking and monitoring, which can prevent serious complications.
The Role of AI & ML in Digital Health
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming industries across the globe, and healthcare is no exception. With the growing need for remote healthcare services, these technologies are playing a crucial role in revolutionizing diagnosis, treatment, and patient management. Let’s understand this from an example of how AI and ML are reshaping remote healthcare with real-world examples.
In the quiet hills of a rural community, Maria faced a daunting challenge. At 58, she received a breast cancer diagnosis that felt like a devastating earthquake in her peaceful life. Limited by her remote location and scarce medical resources, Maria worried about her treatment options.
Then, technology became her unexpected ally. IBM Watson, an intelligent medical assistant, stepped in like a digital guardian angel. By meticulously analyzing Maria’s medical records, genetic data, and comprehensive medical literature, Watson transformed complex medical information into clear, personalized recommendations.
Her local oncology team, armed with Watson’s insights, crafted a precise treatment strategy. What once seemed impossible—receiving world-class medical guidance in a small, isolated community—became a reality. Watson bridged the healthcare divide, turning Maria’s uncertainty into hope.
Through this innovative approach, the technology proved it could reach beyond geographical limitations, delivering compassionate, intelligent healthcare where it was needed most.
Telemedicine Bridging Gaps in Remote Areas
Telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare delivery, especially in remote and underserved regions where medical resources are scarce. By leveraging digital communication technologies, patients can now connect with healthcare professionals across vast distances, breaking down geographical barriers that once limited medical access.
Doctors conduct virtual consultations, diagnose conditions, and provide expert guidance through video calls, mobile apps, and secure messaging platforms. Rural communities, previously isolated from specialized medical care, now receive timely diagnoses, follow-up treatments, and continuous health monitoring.
Patients save time and travel expenses while gaining access to a broader network of medical expertise. This digital healthcare transformation isn’t just about convenience—it’s about ensuring equitable medical support for every individual, regardless of their location or socioeconomic background.
Integrating Wearable Devices into Modern Health Management Strategies
Wearable devices are transforming personal health management, turning individuals into active participants in their wellness journey. These smart technologies—from fitness trackers to advanced medical sensors—continuously monitor crucial health metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, sleep patterns, and activity levels.
Patients with chronic conditions can now receive real-time health insights, enabling early detection of potential medical issues and proactive interventions. For healthcare providers, these devices offer unprecedented access to comprehensive patient data, allowing more personalized and precise treatment strategies.
By bridging the gap between traditional medical checkups, wearables empower people to understand their bodies better, make informed lifestyle choices, and collaborate more effectively with medical professionals in maintaining optimal health.
The Impact of Digital Health on Healthcare Costs
The impact of digital health on healthcare costs is profound, leading to significant savings and improved efficiency. For instance, the integration of telemedicine has transformed how patients access care. A study showed that telehealth visits can cost approximately $40 compared to an average in-person visit of $150.
This shift not only reduces out-of-pocket expenses for patients but also minimizes the burden on healthcare facilities. Furthermore, remote monitoring technologies enable continuous tracking of chronic conditions, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent costly hospitalizations.
For example, a diabetic patient using a remote monitoring system can receive alerts about abnormal blood sugar levels, prompting early adjustments in treatment. This proactive approach not only enhances patient outcomes but also significantly reduces overall healthcare spending. As digital health continues to evolve, its ability to streamline processes and lower costs will be crucial in shaping the future of healthcare delivery.
Understanding Patient Data Privacy & Security in Digital Health
In the digital health era, patient data privacy and security are critical concerns as healthcare systems embrace mobile technologies, cloud computing, and connected devices. These advancements offer improved care and research capabilities, but they also expose sensitive health information to various risks.
Data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access are increasingly common threats. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of patient data requires robust security measures that protect it from the point of collection to its final destination.
Translational researchers, who handle this data, must be equipped with cyber-situational awareness and privacy practices to mitigate these risks, understanding the responsibilities they hold as data owners and ensuring compliance with evolving privacy regulations.
Digital Health Barriers: What You Need to Know
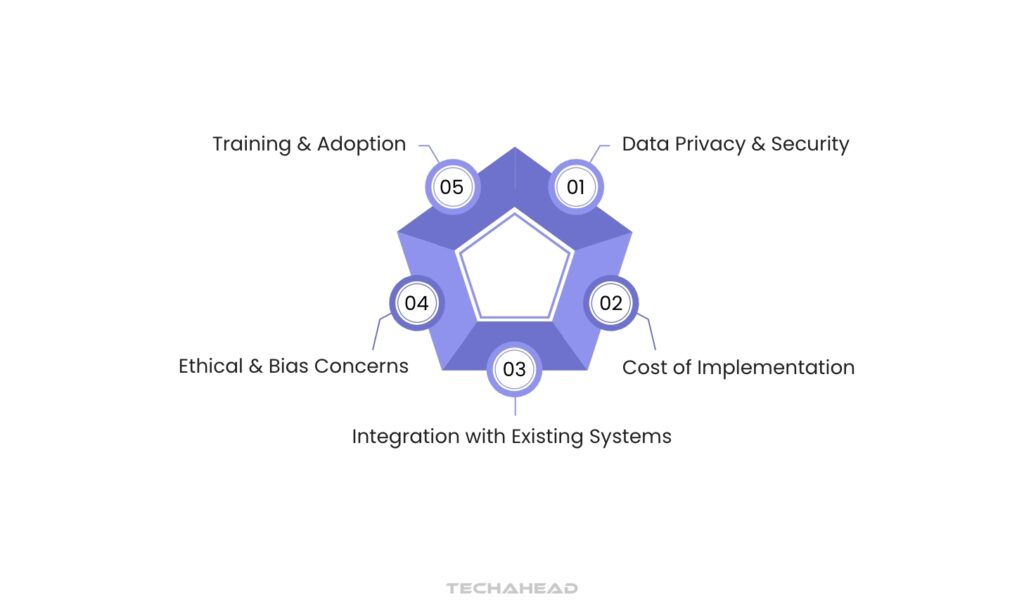
Data Privacy & Security
Protecting sensitive patient information is paramount. For example, while telemedicine platforms like Doxy.me offer convenience, they must ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA to safeguard data.
Integration with Existing Systems
Many healthcare organizations struggle to integrate new digital tools with legacy systems. For instance, a hospital using outdated electronic health records (EHR) may find it difficult to adopt AI-driven solutions effectively.
Cost of Implementation
The initial investment for digital health technologies can be substantial. A small clinic may hesitate to adopt remote monitoring systems due to high upfront costs, despite potential long-term savings.
Training & Adoption
Staff may require extensive training to use new technologies effectively. For example, if a hospital implements a new telehealth system, clinicians need training on how to conduct virtual visits efficiently.
Ethical & Bias Concerns
AI systems can perpetuate biases if trained on unrepresentative data. This could lead to disparities in care, highlighting the need for diverse datasets in developing AI algorithms.
The Future of Digital Health: Emerging Trends and Technologies
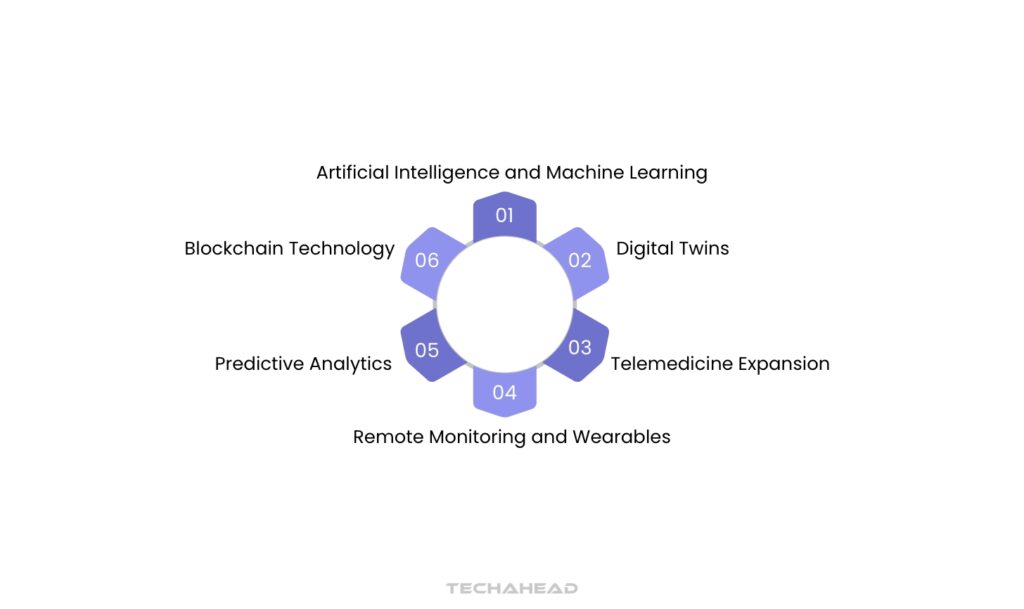
The future of digital health is poised for transformative advancements, driven by emerging trends and technologies that promise to enhance patient care and streamline healthcare delivery. Here are some key developments shaping this landscape:
Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical entities, including patients. By creating a digital twin of a patient, healthcare providers can simulate various treatment scenarios and predict outcomes based on individual health data. For example, a digital twin could help in planning surgeries by modeling how a patient’s body will respond to different interventions, leading to more personalized and effective treatment strategies.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing diagnostics and patient management. These technologies enable faster analysis of medical imaging, identifying conditions such as tumors or fractures with remarkable accuracy. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze X-rays in real-time, providing radiologists with immediate insights that improve diagnostic speed and precision.
Remote Monitoring and Wearables
Wearable devices equipped with sensors allow for continuous health monitoring outside traditional clinical settings. These devices can track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, alerting both patients and providers to potential health issues before they escalate. For example, a smartwatch that monitors heart rhythms can notify users of irregularities, prompting timely medical intervention.
Telemedicine Expansion
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, making healthcare more accessible than ever. AI-driven telehealth platforms can triage patients based on symptoms and provide virtual consultations, reducing the need for in-person visits while maintaining quality care. This trend is expected to continue growing as more patients embrace the convenience of remote healthcare.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast patient outcomes, allowing for proactive interventions. For example, AI models can identify patients at high risk for complications related to chronic diseases such as diabetes or heart disease, enabling healthcare providers to implement preventive measures tailored to individual needs.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent methods for managing patient data. By ensuring data integrity and privacy, blockchain can facilitate seamless sharing of medical records across different providers while maintaining patient confidentiality.
Why Healthcare Providers Should Embrace Digital Health Technologies
Adopting digital health tools offers numerous benefits for healthcare providers, enhancing both operational efficiency and patient outcomes. For instance, telemedicine platforms allow providers to reach patients remotely, reducing wait times and increasing access to care, particularly in underserved areas.
A study showed that telehealth consultations can decrease patient no-show rates by up to 30%, ensuring more consistent care. Additionally, AI-driven diagnostic tools can analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy, helping radiologists identify conditions like tumors earlier than traditional methods. This not only improves patient prognosis but also optimizes resource allocation within healthcare facilities.
Furthermore, wearable devices enable continuous monitoring of chronic conditions, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent hospitalizations. By integrating these digital health solutions, healthcare providers can enhance patient engagement, streamline workflows, and ultimately deliver higher quality care while reducing costs associated with in-person visits and late-stage interventions.
Digital Health and the Role of Government Regulations
In the U.S., consumer devices fall under the regulatory framework of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA), which classifies them based on risk levels.
The FDA oversees medical devices, ensuring safety and effectiveness through a tiered system: Class I (general controls), Class II (general controls and special controls), and Class III (general controls and premarket approval).
Additionally, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) enforces laws against unfair trade practices, safeguarding consumer interests. The Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) plays a broader role in public health, with the FDA as its primary regulatory body for food, drugs, and devices.
The Digital Health Center of Excellence within the FDA focuses on digital health technologies, providing regulatory support in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and real-world evidence. By navigating these regulations, healthcare providers can ensure compliance while leveraging innovative digital health solutions to enhance patient care.
Conclusion
Digital health is fundamentally transforming modern healthcare, driving innovation and improving patient outcomes. As technologies like AI, telemedicine & wearable devices become increasingly integrated into healthcare systems, they enhance accessibility, streamline processes, and promote personalized care. These advancements not only empower patients to take control of their health but also enable providers to deliver more efficient and effective services. Looking ahead, the continued evolution of digital health tools will play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare, ensuring that it remains responsive to the needs of patients while addressing the challenges of an ever-changing landscape. Embracing these innovations is essential for creating a more equitable and efficient healthcare system for all.
FAQs
Digital health tools help people with chronic illnesses track symptoms, medications, and health data, allowing better self-management and reducing potential medical complications
Massive health information gathering helps doctors spot patterns, predict risks, and customize treatments by examining extensive medical records, ultimately enhancing patient care and detecting potential health challenges.
Digital apps now help people with mental health challenges track moods, access therapy, practice meditations, and find support, making mental wellness resources more accessible and convenient.