The global healthcare sector is grappling with unprecedented pressures and transformations. Today, challenges span affordability, shifting patient expectations, and ever-rising costs. As these demands intensify, innovative solutions are not just desirable—they’re imperative. To address these growing concerns, the healthcare ecosystem must pivot toward modernized strategies.
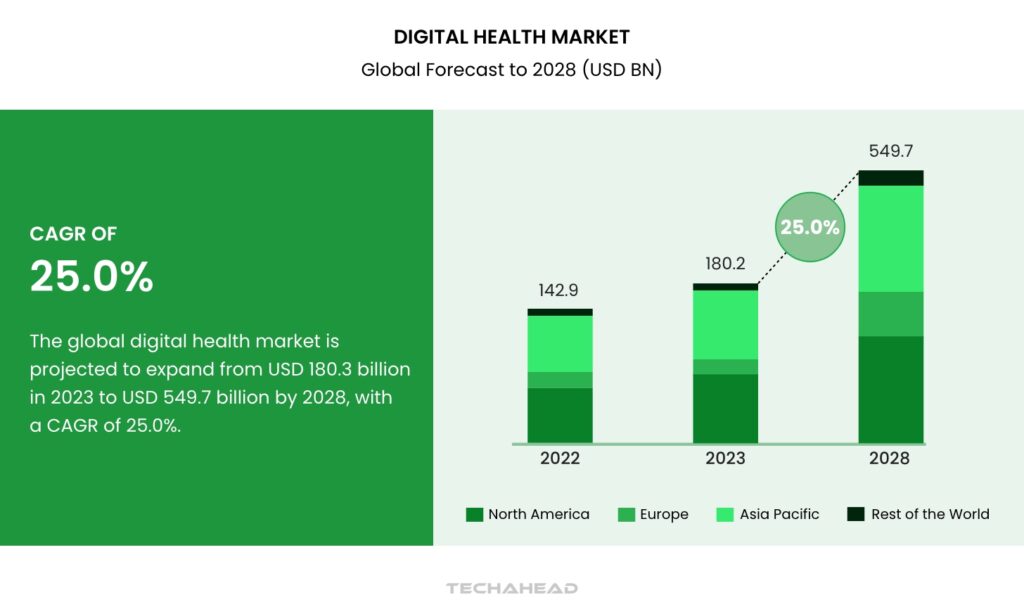
The global digital health market is projected to surge from $180.2 billion in 2023 to $549.7 billion by 2028, reflecting a robust CAGR of 25%. Key growth drivers include the rising adoption of smartphones, tablets, and mobile platforms, alongside supportive initiatives and expanding strategic partnerships. Additionally, an aging population, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and a stronger emphasis on patient-centric healthcare solutions are fueling this market’s rapid expansion.
MedTech and Pharma sectors, in particular, face increasing demands to refine their R&D capabilities, evolve service models, and enhance treatment options. This transformation requires embracing digital technology and shifting toward a more patient-centric approach that emphasizes ambulatory and at-home care.
Digital innovation offers clear and impactful benefits, from increased efficiency to personalized patient experiences. However, understanding the driving forces behind this digital shift is crucial. Equally important is recognizing the barriers that may hinder its full adoption. To gain comprehensive insights, we’ve delved deeper into the complexities of these forces and the challenges that lie ahead in reshaping healthcare.
The Landscape of Digital Health and MedTech
Understanding Digital Health
Digital health encompasses a broad range of technologies, from mobile health apps to advanced telemedicine systems. These solutions aim to improve patient outcomes, simplify access to healthcare, and empower patients to take charge of their health. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), wearable health trackers, and telemedicine platforms enable real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and remote patient care, offering healthcare providers insights that were previously unavailable.
The MedTech Revolution
MedTech, or medical technology, is a field focused on creating devices and tools that improve medical processes, diagnostics, and treatments. With breakthroughs in minimally invasive surgeries, robotic-assisted procedures, and digital imaging, MedTech is enhancing patient care on a global scale. Unlike digital health solutions that focus on software, MedTech often combines hardware innovations with digital capabilities, making it a crucial element in healthcare’s digital transformation.
Key Drivers of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
The key drivers of digital transformation in digital health and MedTech include rising consumer expectations for personalized, accessible care; regulatory pressures for data protection and transparency; and advances in AI, machine learning, and big data. Together, these forces push the healthcare industry towards models that focus on quality, affordability, and convenience.
The Process of Digital Health Transformation
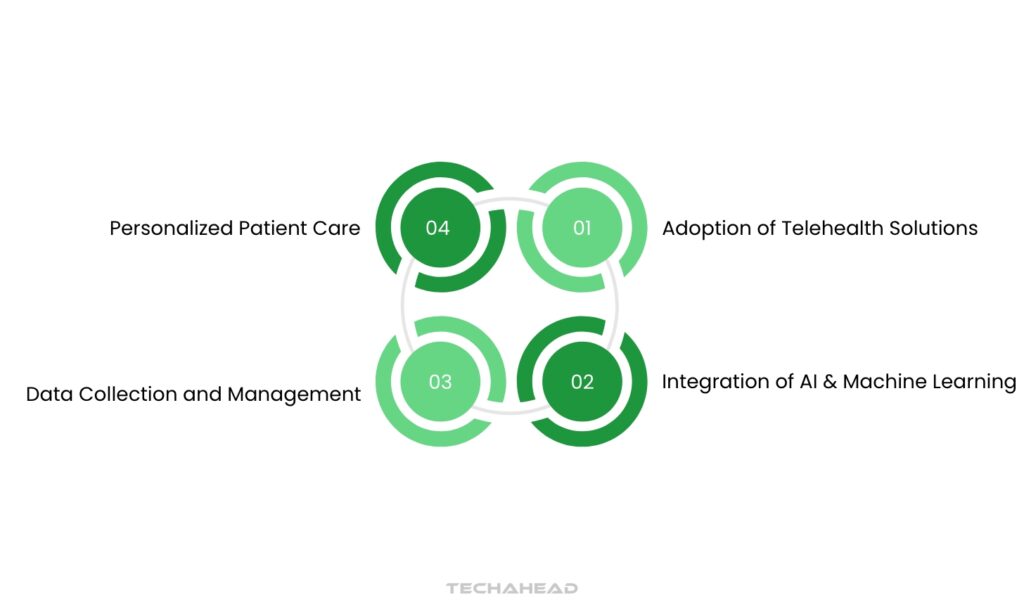
Adoption of Telehealth Solutions
Telehealth has been a cornerstone of digital health transformation. By enabling virtual consultations, telehealth solutions make it easier for patients to receive care without geographical barriers. Healthcare providers are now integrating telehealth as a permanent service by setting up secure digital platforms, ensuring patient data protection, and training staff on telehealth tools.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming diagnostics, treatment planning, and personalized patient care. From predictive algorithms for disease progression to chatbots that support mental health, AI is enabling rapid, accurate, and data-driven healthcare solutions. However, implementing AI in healthcare requires a robust framework that prioritizes ethical considerations, training, and ongoing evaluation to ensure accuracy and trustworthiness.
Data Collection and Management
Data is central to digital health, as healthcare providers increasingly rely on electronic medical records (EMRs), wearable devices, and patient self-reports. Integrating this data across platforms enables providers to gain holistic insights into a patient’s health. Ensuring interoperability and data privacy is essential, as healthcare systems must work across providers, apps, and devices while safeguarding sensitive information.
Personalized Patient Care
Digital health has shifted care models from reactive to proactive. Predictive analytics and personalized health plans allow healthcare providers to deliver individualized treatment and identify health issues before they escalate. This shift helps reduce hospitalizations, improve outcomes, and empower patients to manage chronic conditions with support from digital health tools.
Benefits of Digital Health Transformation
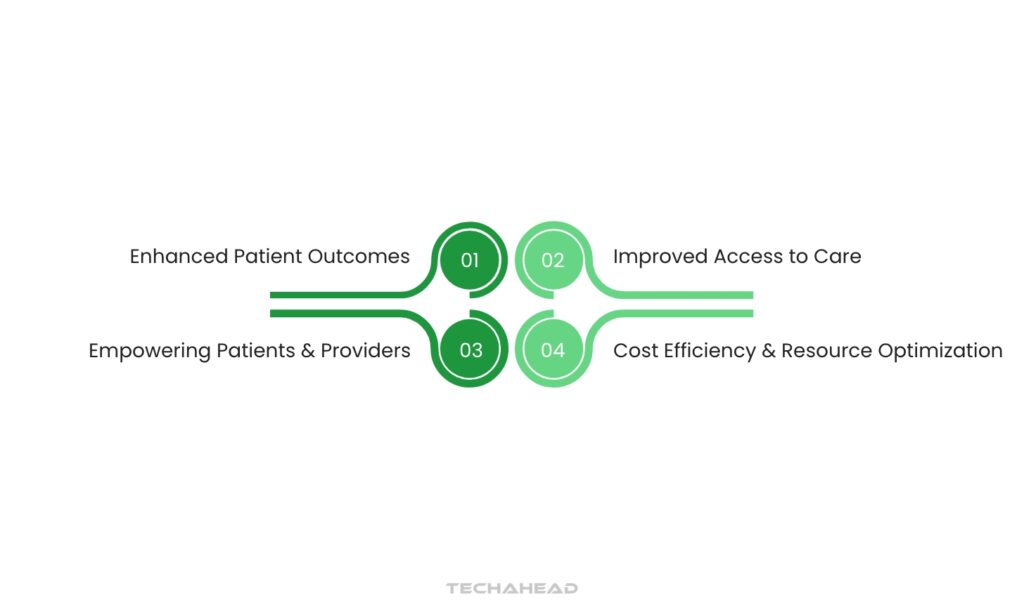
Enhanced Patient Outcomes
Digital health tools contribute to improved patient outcomes by enabling early diagnosis and treatment. For example, wearables monitor vital signs in real-time, allowing healthcare providers to identify abnormalities quickly. AI algorithms can analyze imaging data for faster, more accurate diagnoses, leading to early interventions that improve recovery rates and long-term health.
Improved Access to Care
By providing digital access points such as telemedicine, healthcare can reach underserved populations, including those in rural or low-income areas. Telemedicine bridges geographical gaps, ensuring that patients have access to consultations, follow-ups, and specialist advice, regardless of location.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
By providing digital access points such as telemedicine, healthcare can reach underserved populations, including those in rural or low-income areas. Telemedicine bridges geographical gaps, ensuring that patients have access to consultations, follow-ups, and specialist advice, regardless of location.
Empowering Patients and Providers
Digital health solutions empower patients by giving them access to their health data, enabling self-care, and improving communication with healthcare providers. Patients who use digital tools are often more engaged, leading to better adherence to treatments and health recommendations.
Challenges in Digital Health and MedTech Transformation
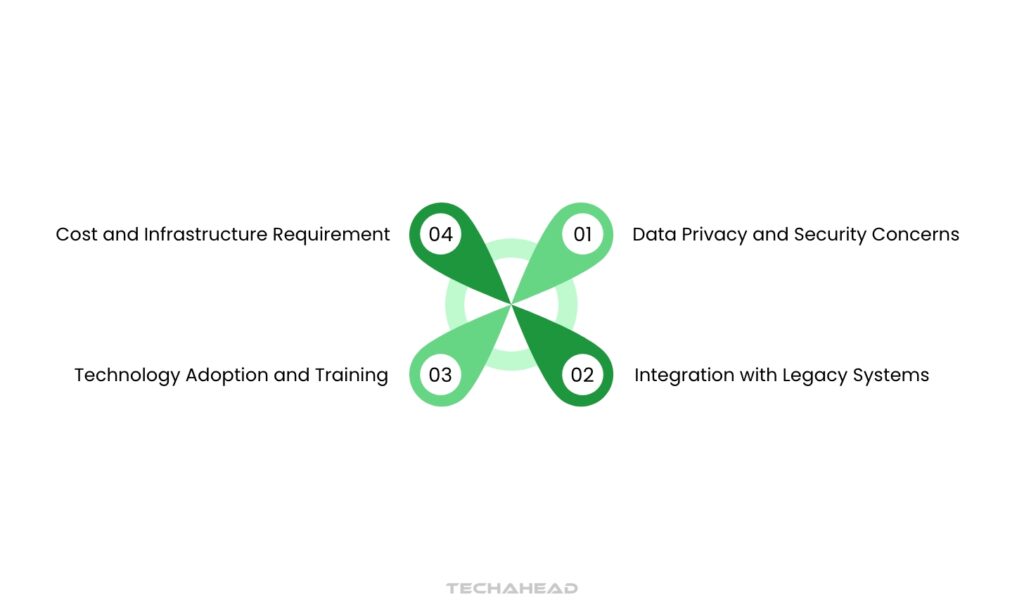
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Data privacy remains a significant concern, especially as healthcare providers collect more patient data. Regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe enforce strict guidelines on data handling and patient consent. Ensuring data security requires sophisticated cybersecurity measures and rigorous adherence to regulatory standards to build patient trust.
Integration With Legacy Systems
Many healthcare providers still operate on legacy systems that lack interoperability with new digital tools. Integrating modern solutions with outdated systems can create data silos and hinder the seamless flow of information, impacting the quality of patient care. A phased approach to modernization, with support from IT specialists, can help address this challenge.
Technology Adoption and Training
Resistance to new technology among healthcare providers can hinder the adoption of digital health solutions. Providers may need extensive training to understand and use digital tools effectively. Healthcare organizations should invest in change management and training programs to encourage acceptance and minimize disruptions.
Cost and Infrastructure Requirement
The initial costs of implementing digital solutions, along with infrastructure needs, can be prohibitive, particularly for smaller healthcare providers. While the return on investment is clear, overcoming these initial financial and logistical barriers remains a challenge.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
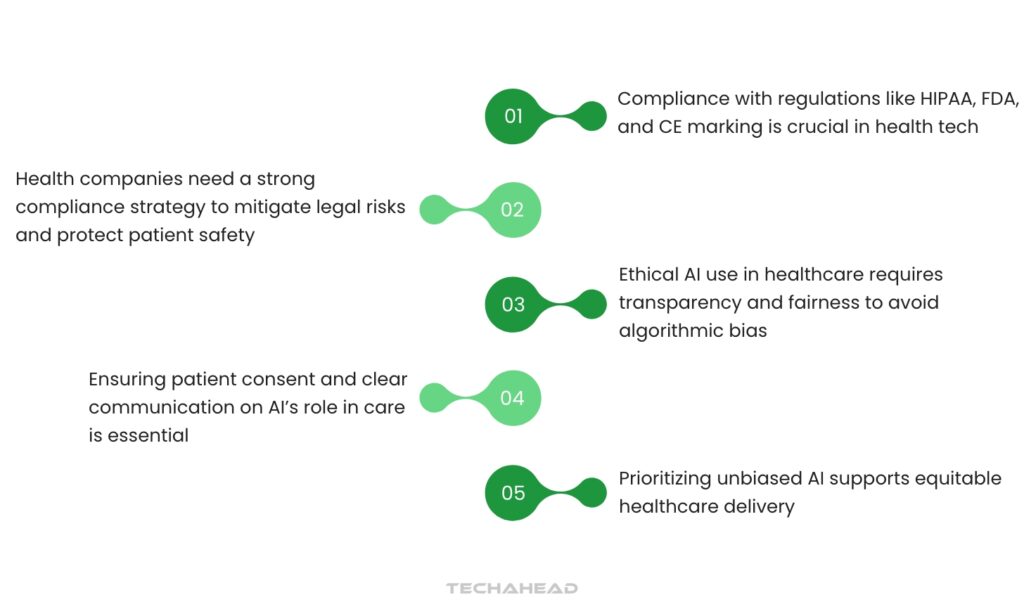
Navigate Regulatory Compliance
Navigating healthcare regulations is complex, with guidelines and requirements that vary by country and region. Health tech companies must comply with regulatory standards like HIPAA, FDA approvals, and CE marking, depending on where they operate. A robust compliance strategy is essential for any organization deploying digital health solutions to avoid legal risks and ensure patient safety.
Ethical Implications of AI in Healthcare
AI in healthcare presents ethical considerations, such as bias in algorithms and patient consent for AI-assisted diagnosis. Ensuring fairness and transparency in AI algorithms is essential, as biased AI could result in health disparities. Additionally, patients should be informed about the role of AI in their care, and health providers must prioritize transparent AI usage.
The Future of Digital Health and MedTech
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Emerging technologies like 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) are expected to drive digital health forward. 5G connectivity will support the use of IoT in healthcare, enabling faster, more reliable data exchange between devices. Additionally, innovations in precision medicine and genomics will bring us closer to truly personalized healthcare.
Predictions for the Next Decade
In the coming decade, we can expect digital health and MedTech to redefine healthcare by focusing on patient-centered care. AI will play a more prominent role, from diagnostics to treatment planning, while telehealth will become integral to regular care delivery. Digital solutions will be critical in managing chronic diseases, and advanced data analytics will help predict patient outcomes more accurately.
Conclusion
Digital health and MedTech are at the forefront of a transformative era in healthcare, redefining how patients interact with providers, how data is utilized, and how care is delivered. As these technologies evolve, they offer unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes, increase access to care, and make healthcare more efficient and affordable.
However, to fully realize the potential of these innovations, healthcare organizations must address key challenges, including data privacy, integration with legacy systems, and regulatory compliance. By adopting a patient-centric approach, investing in training, and fostering strategic partnerships, the healthcare industry can overcome these obstacles and embrace the future with confidence. Now is the time for healthcare providers, policymakers, and tech innovators to collaborate and leverage these powerful tools to deliver exceptional care and address the ever-growing demands of modern healthcare.

FAQs
Digital health encompasses technologies like mobile apps, telemedicine, and AI-driven tools to support patient care and healthcare delivery, focusing on software-based solutions. MedTech, on the other hand, involves medical devices and equipment, including robotics and digital imaging, that enhance treatment and diagnosis, often combining hardware and digital technology.
Digital health tools, such as wearables and AI-driven diagnostics, enable early detection of health issues, personalized treatment plans, and continuous monitoring. These technologies allow for proactive intervention, reducing the need for hospitalization and enhancing recovery rates, ultimately improving long-term patient outcomes.
The primary challenges include ensuring data privacy and security, integrating new digital tools with existing legacy systems, managing the costs associated with implementation, and training staff to adapt to new technologies. These challenges must be addressed to ensure a smooth transition to digital healthcare.
AI in healthcare raises concerns about data privacy, algorithm bias, and informed consent. Ensuring that AI algorithms are fair and transparent is essential to prevent disparities in care, and patients should be aware of and consent to AI’s role in their care decisions.
Future trends include the expansion of 5G and IoT, enabling faster, more reliable data transmission; advancements in personalized medicine and genomics; and greater integration of AI in diagnostics and treatment. These trends are expected to make healthcare more accessible, personalized, and efficient in the years to come.